Any conic may be determined by three. Identify a conic in polar form. Web conic sections in polar coordinates. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola,. Web to work with a conic section written in polar form, first make the constant term in the denominator equal to 1.
To convert this cartesian equation to polar form, we will use the substitutions and. First, we should expand the expression: Web find the polar form of a conic given a focus at the origin, \(e=\dfrac{3}{5}\), and directrix \(x=4\). Identify a conic in polar form.
Identify a conic in polar form. Polar coordinates allow you to extend your knowledge of conics in a new context. Any conic may be determined by three characteristics:
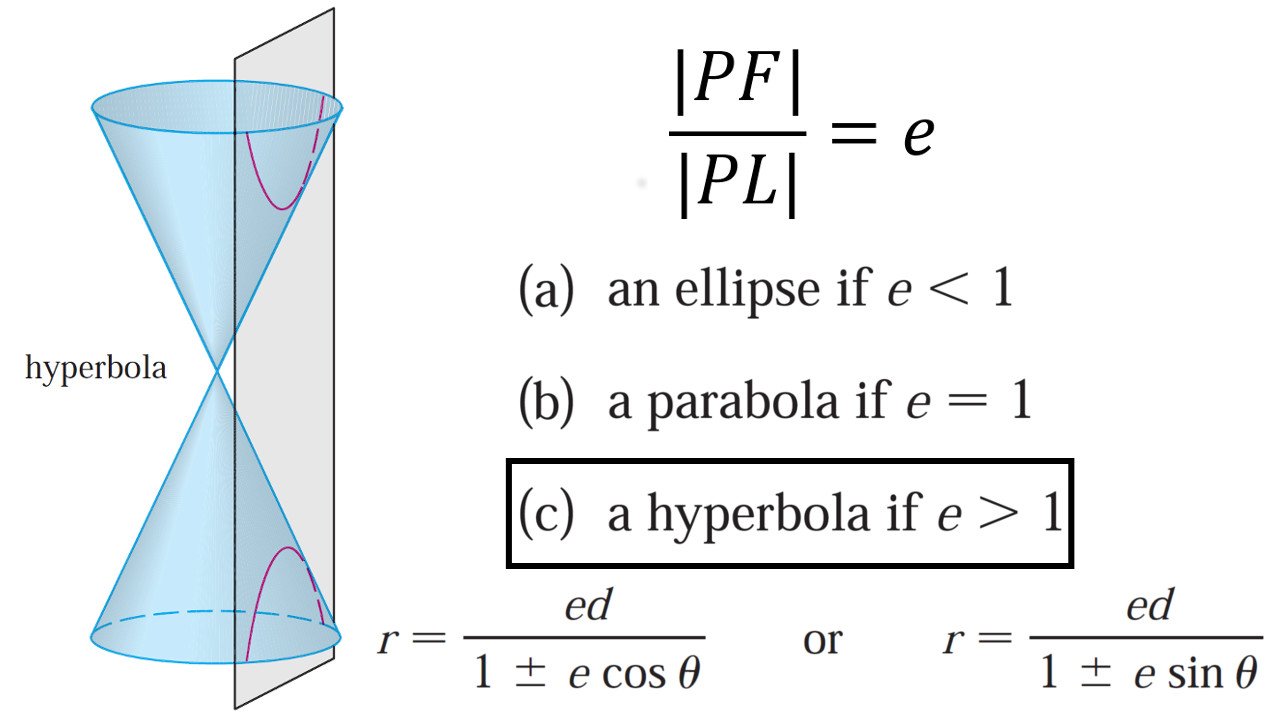
Web each of these orbits can be modeled by a conic section in the polar coordinate system. I am not sure that your canonical form is correct because you didn't define x ′ and y ′. If e = 1, the conic is a parabola. Web conic sections in polar coordinates | precalculus. By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Web introduction to conic sections in polar coordinates | college algebra. Solution because the directrix is \(x=p\), we know the function in the denominator is cosine. If e = 1, the conic is a parabola.
Polar Coordinates Allow You To Extend Your Knowledge Of Conics In A New Context.
Web identifying a conic in polar form. Any conic may be determined by three characteristics: By the end of this section, you will be able to: If the directrix is a distance d d away, then the polar form of a conic section with eccentricity e e is.
Graph The Polar Equations Of Conics.
R(θ) = ed 1 − e cos(θ − θ0), r ( θ) = e d 1 −. First, we should expand the expression: Web identifying a conic in polar form. Any conic may be determined by three characteristics:
This Can Be Done By Dividing Both The Numerator And The.
Web introduction to conic sections in polar coordinates | college algebra. Web to work with a conic section written in polar form, first make the constant term in the denominator equal to 1. Define conics in terms of a focus. If e > 1, the conic is a hyperbola.
Solution Because The Directrix Is \(X=P\), We Know The Function In The Denominator Is Cosine.
If e = 1, the conic is a parabola. Any conic may be determined by three. A single focus, a fixed line called the directrix, and the ratio of the. Web each of these orbits can be modeled by a conic section in the polar coordinate system.
Web if 0 < e < 1, the conic is an ellipse. Web to work with a conic section written in polar form, first make the constant term in the denominator equal to 1. Web in geometry, conic sections are curves produced when a right circular cone intersects with a plane. A single focus, a fixed line called the directrix, and the ratio of the distances of each to a. To convert this cartesian equation to polar form, we will use the substitutions and.